Dust Rotational Dynamics and Stellar Feedback
Very large molecules, nanoparticles, and dust grains (hereafter referred to as cosmic dust) play important role in astrophysics. I study how cosmic dust interact with ambient environments, spun-up to rapid rotation, and the resulting effects of superfast grain rotation on the grain structure and molecules frozen on the grain surface. We identified important effect of stellar feedback from cosmic transients including supernova, Gamma-ray burst, and kilonova on surrounding dust.

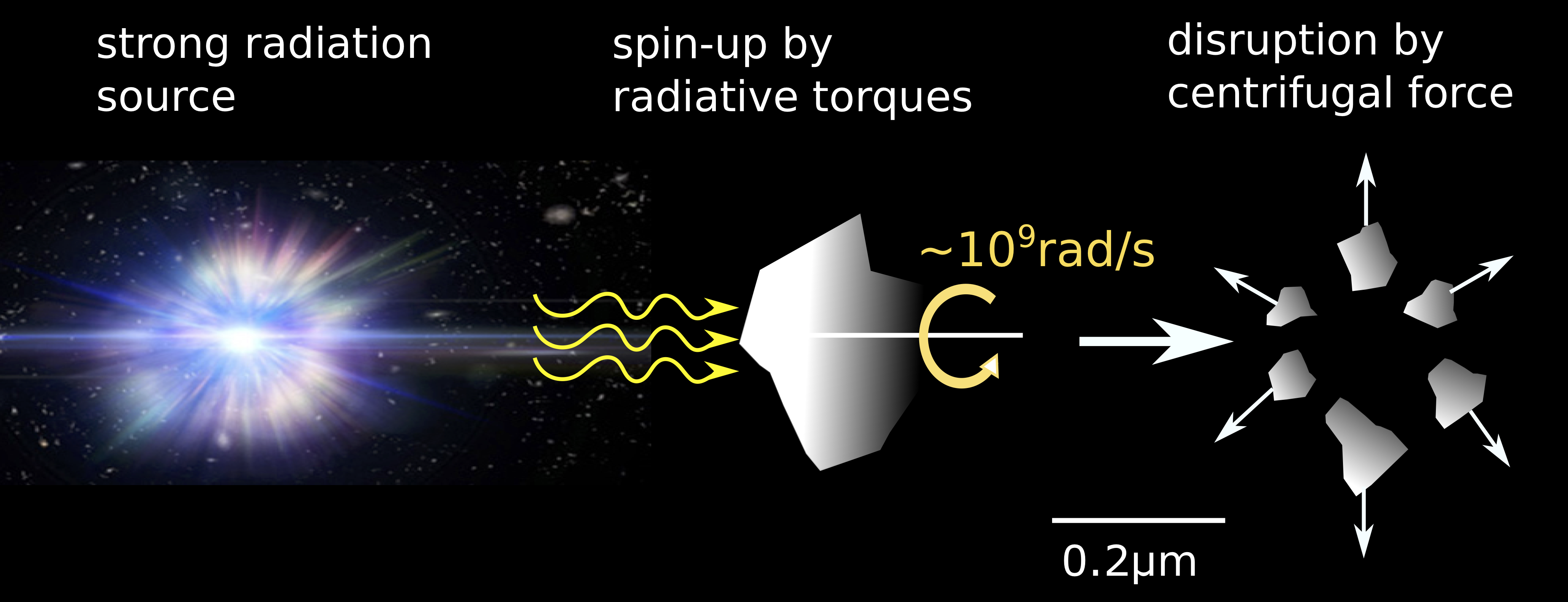
Rotational Disruption of Grains by Radiative Torques
Hoang et al. discovered that grains near a strong radiation source can be spun-up to extremely fast rotation at billion rounds per second, such that centrifugal force can instantaneously disrup the grain into small fragments. This is a new mechanism to destroy dust grains by strong radiation fields based on the principle of centrifugal force within a spining body, which we term Radiative Torque Disruption (RATD) mechanism. We are exploring many effects of centrifugal force due to rapid rotationi.
Rotational Disruption of Nanoparticles in Shocks
We study rotation of nanoparticles in shocks and discovered that smallest nanoparticles are disrupted by centrifugal forces due to extremely fast rotation.
Rotational Desorption of Complex Molecules from Grain Surface
We study the effect of suprathermal rotation on desorption of molecules from the grain surface in star-forming regions. We discover a new process that can desorb molecules at lower temperatures than the popular thermal desorption mechanism.